Types of CRM Software: A Complete Guide to Choosing the Right CRM for Your Business
Today, types of CRM software vary widely in features and use cases—from sales and marketing automation to comprehensive customer relationship management. In this article, GMO-Z.com RUNSYSTEM walks you through the advantages and disadvantages of each CRM system and provides guidance on selecting the right solution for your business. The goal is to streamline processes, improve sales performance, and enhance the overall customer experience.
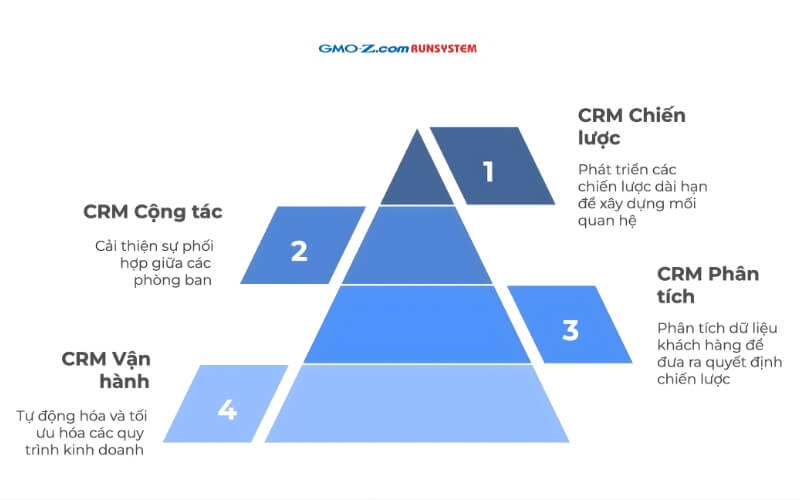
Quick summary 4 main types of CRM systems: Operational CRM, Analytical CRM, Collaborative CRM, and Strategic CRM Vietnamese businesses typically need one of the following:
|
1. Popular types of CRM software today
Below are the most commonly used types of CRM software, along with an overview of their core functionalities:
1.1. Operational CRM
Operational CRM focuses on automating and optimizing customer-facing processes, including sales, marketing, and after-sales service. This type of CRM system helps businesses improve operational efficiency and deliver better customer experiences.
Key features:
- Sales automation: Manage leads, track opportunities, and generate quotes automatically.
- Contact management: Store customer information, interaction history, and preferences.
- Service management: Support ticketing, live chat, and knowledge bases to resolve issues quickly.
Implementing an operational CRM system helps reduce manual work, save time, and focus on building long-term customer relationships.
1.2. Analytical CRM
Analytical CRM focuses on collecting, processing, and analyzing customer data. It enables businesses to understand customer behavior, needs, and trends, supporting more accurate strategic decision-making.
Key features:
- Data mining: Identify patterns and trends in customer behavior.
- Data warehousing: Consolidate and organize data from multiple sources to gain a holistic view.
- Behavioral analytics: Measure conversion rates, customer lifetime value, and satisfaction levels to optimize business strategies.
Analytical CRM helps businesses personalize experiences, increase engagement, and improve overall customer management efficiency.
Read more: What Is a CRM Database? Roles and Best Practices for Building High-Quality Data
1.3. Collaborative CRM
Collaborative CRM focuses on improving coordination between internal teams and external partners, ensuring that all departments share consistent customer information.
Key features:
- Interaction management: Track customer interactions across email, phone, and social media.
- Communication channel management: Coordinate channels to maintain consistent and effective messaging.
- Document management: Store and share customer-related documents for quick and easy access.
A collaborative CRM system enables seamless service delivery, improving customer satisfaction and loyalty.
1.4. Strategic CRM
Strategic CRM focuses on building and maintaining long-term customer relationships, creating sustainable value for the business.
Key features:
- Customer segmentation: Group customers based on characteristics, behaviors, or needs for more effective engagement.
- Engagement strategies: Implement programs and initiatives to increase customer loyalty.
- Customer data management: Collect, store, and protect data to support strategic decision-making.
Strategic CRM helps businesses strengthen customer relationships, drive growth, and achieve sustainable profitability.